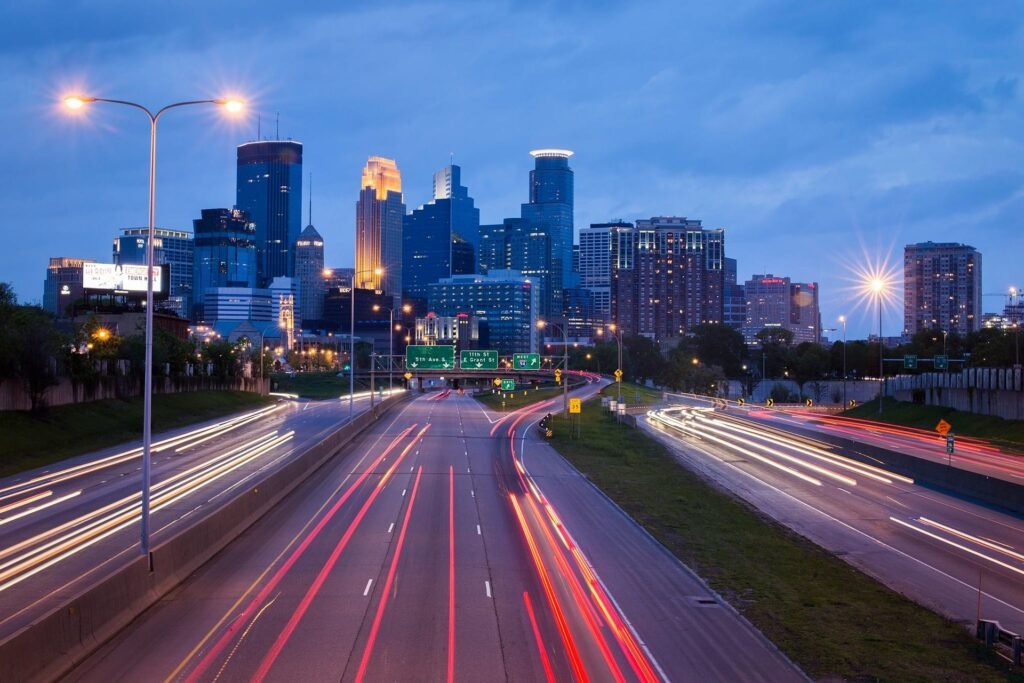
Timer Dimming for LED Street Lights: What Buyers Need to Know (2025 Guide)
What Is Timer-Based Dimmi
ZigBee is a low-power, short-range, and highly scalable wireless communication protocol designed for smart lighting, building automation, and IoT applications. With its self-healing mesh network and secure AES-128 encryption, ZigBee ensures reliable performance across thousands of devices—helping businesses build smarter, more efficient systems.
ZigBee technology is specifically designed to meet the needs of IoT and smart lighting applications, where devices must run efficiently for long periods under limited power and computing resources. Its self-organizing mesh architecture ensures stability and scalability, making it one of the most reliable choices for large-scale sensor networks.
battery-powered devices can last for months or even years.
ideal for sensor readings, control commands, and automation signals.
up to 100m per device, with mesh networking to extend coverage effortlessly.
if one node fails, data automatically finds another route.
supports networks with over 65,000 devices.
AES-128 encryption ensures safe and reliable communication.


A ZigBee network is built on a hierarchical yet flexible mesh topology, where different devices play unique roles to ensure stability and scalability. Typically, there are three types of nodes within the system:
The “brain” of the network. Responsible for initializing the network, assigning addresses, and managing security. Usually a powered device such as a smart lighting gateway.
Extends the coverage of the network. Acts as a relay, forwarding data between devices. Requires continuous power supply for stable operation.
Battery-powered devices such as sensors, switches, or controllers. Operates mostly in sleep mode to save energy. Communicates only through a router or coordinator.
Together, these roles form a robust and self-healing mesh network capable of supporting large-scale smart lighting and IoT deployments.
Low-power mesh networking for scalable automation across buildings, industry, agriculture, healthcare, and smart cities.
Smart Home & Building Automation
Intelligent lighting systems, switches, door locks, window controls, HVAC monitoring.
Example: Smart bulbs (Philips Hue), security sensors, curtain motors.
Industrial Automation
Real-time equipment monitoring, data collection, and remote control in complex environments.
Mesh networking ensures reliable communication even in noisy industrial sites.
Smart Agriculture
Deployment of soil moisture sensors, light sensors, and irrigation control systems across large fields.
Enables precise monitoring and data-driven farming.
Healthcare Monitoring
Wearable and bedside devices collect patient health data and transmit wirelessly for continuous monitoring.
Smart Cities
Intelligent streetlight management, parking space occupancy detection, environmental monitoring.
ZigBee is built on top of the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, which defines the physical and MAC layers. On this foundation, ZigBee adds advanced networking and application functionalities to create a complete solution for IoT communication.
Physical Layer (PHY)
Handles radio transmission and reception, frequency channels, modulation, and signal strength.
MAC Layer
Manages access to the wireless medium, framing, and error detection.
Network Layer (NWK)
Responsible for device addressing, routing, and mesh networking functions.
Provides ZigBee’s hallmark self-healing and scalable connectivity.
Application Layer (APL)
Defines device profiles, application objects, and communication between end devices.
Ensures interoperability between ZigBee-certified devices.
This layered structure allows ZigBee to focus on network intelligence and device interoperability, while the underlying IEEE 802.15.4 standard guarantees robust wireless communication.
Understanding ZigBee’s strengths and trade-offs helps businesses choose the right IoT technology.
ZigBee is most effective for low-data, energy-efficient, and large-scale IoT networks where reliability and long-term operation matter more than bandwidth.
Comparing wireless technologies to help you choose the right solution for IoT and smart automation.
| Feature | ZigBee | WiFi | Bluetooth (BLE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption | Ultra-low | Very high | Low |
| Data Rate | Up to 250 kbps | High (hundreds of Mbps) | Medium (1–2 Mbps) |
| Range | 10–100 m (mesh extendable) | Medium (router dependent) | Short (~10 m) |
| Network Size | 65,000+ devices | Small (<50) | Small |
| Best Applications | IoT sensors, automation, smart lighting, smart cities | Internet access, video, high bandwidth | Wearables, audio, personal connectivity |
ZigBee is ideal for large-scale, low-power IoT networks.
Choose WiFi for high-speed internet, or Bluetooth for short-range personal devices.
ZigBee is not designed for high-speed data transfer, but it excels in what matters most for IoT and smart automation:
Energy efficiency – enabling devices to operate for years on small batteries.
Massive scalability – supporting networks with tens of thousands of nodes.
Reliable mesh networking – ensuring strong coverage and self-healing connections.
Enhanced security – AES-128 encryption and authentication for safe operation.
With the improvements of ZigBee 3.0, interoperability across devices from different manufacturers has been greatly enhanced, making it easier to deploy and manage large IoT ecosystems.
For businesses and cities planning smart lighting, industrial automation, agriculture monitoring, or smart building systems, ZigBee provides a cost-effective and reliable foundation to scale up with confidence.
MVS delivers a complete range of outdoor lighting solutions designed for durability and performance. With advanced optics, IP65 & IK10 protection, and certified quality, our products cover everything from modular floodlights and high-mast systems to smart-control street lighting (DALI/DMX512/0-10V). Whether for roads, stadiums, ports, or industrial areas, MVS ensures uniform brightness, stable operation, and long service life. By choosing MVS, you gain not only reliable hardware but also engineering support and project-specific customization, helping your projects meet professional standards and long-term efficiency.






Our catalog offers modular, energy-saving, and high-performance LED solutions. Share your project needs, and we’ll create a tailored lighting plan for you.



For more professional knowledge and practical guidance, visit our blog to discover in-depth articles on LED street lights and project solutions.
What Is Timer-Based Dimmi
Outdoor Lighting Installa
Introduction – Why Upgrad

Introduction As cities an
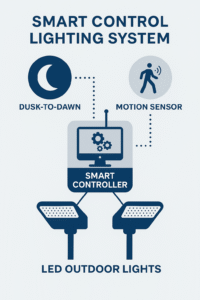
Introduction Outdoor ligh
How to Waterproof LED Lig
Select the topic that best fits your project needs.
Smart Control Systems and Standards:
[Smart Lighting System] | [Central Control System] | [Automatic Scene Control] | [Smart Gateway] | [LoRa System] | [Bluetooth Control System] | [Zigbee] | [Zhaga] | [NEMA]
Lighting Control and Dimming Methods:
[DMX512] | [DALI Dimming] | [Timer Light] | [0-10V Dimming] | [Single Color Dimming] | [Sensor Control] | [Smart Control Systems] | [IoT Lighting System]
View the complete Smart Lighting Knowledge Hub for more topics.